
Machined parts are polished to achieve a smooth, mirror-like surface, removing tool marks and improving visual appearance.
Polishing is a surface finishing process used to improve the smoothness, gloss, and appearance of CNC machined parts. It also reduces surface roughness, removes tool marks, and prepares parts for further surface treatments such as anodizing or coating.




Utilizes rotating cutting tools for high-precision machining of flat surfaces, curves, and complex parts, ideal for mold making, aerospace, and automotive industries.

Uses rotating workpieces and cutting tools for efficient machining of cylindrical components, widely applied in shafts, discs, and precision parts manufacturing.

Enables multi-angle precision cutting, reducing setups and machining complex surfaces, perfect for high-end aerospace, medical devices, and precision mold manufacturing.






Cause:Inconsistent polishing pressure, tool angle, or polishing time.
Impact:Leads to uneven gloss or visible patches on the part surface.

Cause:Excessive polishing time or using overly fine abrasive compounds.
Impact:May cause dimensional deviation or deformation of thin-walled areas.

Cause:Incomplete cleaning after polishing.
Impact:Residues may cause surface stains, oxidation, or interfere with coating adhesion.

Cause:Using contaminated polishing pads or improper polishing motion.
Impact:Visible lines or swirl marks reduce surface quality and appearance.

Cause:Overheating during polishing or inadequate cleaning before storage.
Impact:Causes dull or yellowish appearance, requiring re-polishing or rework.

Cause:Dust, oil, or polishing paste residue not fully removed before or during polishing.
Impact:Causes surface stains, dull spots, or uneven reflection, especially visible after anodizing or coating.
| 01 | Surface Preparation Removes oil, dust, and machining residues to ensure a clean surface before polishing. Typical Parameters: Alkaline wash 50–70 °C, 5–10 min. Standards: In-house PL-SOP-01; | Standards: In-house PL-SOP-01; | |
| 02 | Rough Polishing Removes machining marks and surface unevenness using abrasive wheels or compounds. Typical Parameters: Sisal wheel, brown or black polishing compound. Standards: In-house PL-SOP-02; | Standards: In-house PL-SOP-02; | |
| 03 | Intermediate Polishing Refines surface texture, transitioning from coarse to fine abrasives for smoother finish. Typical Parameters: Medium-speed polishing, compound grain size 800–1000#. Standards: In-house PL-SOP-03; | Standards: In-house PL-SOP-03; | |
| 04 | Fine Polishing Achieves mirror-like gloss using soft wheels and fine polishing paste. Typical Parameters: Cotton or flannel wheel, white compound. Standards: In-house PL-SOP-04; | Standards: In-house PL-SOP-04; | |
| 05 | Cleaning & Inspection Removes residual compounds, checks for scratches or swirl marks. Typical Parameters: Ultrasonic cleaning 5–10 min, visual inspection under 500 lux. Standards: In-house PL-SOP-05; | Standards: In-house PL-SOP-05; | |
| 06 | Surface Protection Applies anti-oxidation oil or protective film to prevent discoloration during storage. Typical Parameters: Protective oil coating, vacuum sealing, or direct packaging. Standards: In-house PL-SOP-06; | Standards: In-house PL-SOP-06; |

Engine parts, turbine blades, and other high-precision components.

Trim parts, lighting fixtures, and other visible components.

Surgical instruments, implants, and medical devices.

Decorative parts and consumer goods requiring a high-end finish.
Typical polishing grades after CNC machining:
| Finish Type | Roughness (Ra) | Description |
| Matte Polish | 0.8–0.4 μm | Soft sheen, non-reflective |
| Semi-gloss Polish | 0.4–0.2 μm | Uniform brightness |
| Mirror Polish | <0.2 μm | High reflectivity, glossy mirror-like finish |
For high-precision CNC parts, leave a polishing allowance of 0.02–0.05 mm on each surface. This ensures the part reaches the desired finish without affecting final dimensional tolerances.

The polishing quality and achievable surface finish largely depend on the material hardness and microstructure.
Best materials:Aluminum, stainless steel, brass, and copper.
Avoid:Very soft plastics or porous metals—they can deform or trap polishing compounds. For aluminum CNC parts, we recommend 6061-T6 or 7075-T6, as both provide excellent polishability and surface stability.

Good design can significantly improve polishing efficiency and final finish:

Polishing costs depend on several factors:
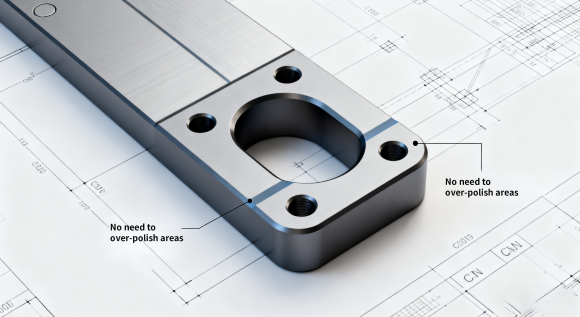
| Property | Typical Range |
| Surface Roughness (Ra) | 0.8 μm – 0.05 μm |
| Finish Levels | Matte / Semi-gloss / Mirror |
| Applicable Materials | Aluminum, Stainless Steel, Brass, Copper, Titanium |
| Tolerance Impact | Slight material removal, typically < 0.01mm |







Send us your part files or design drawings. Our surface finishing experts will evaluate the part geometry, surface requirements, and production volume and recommend the ideal machining process for your CNC machined parts.